Search Results for: homologous structures
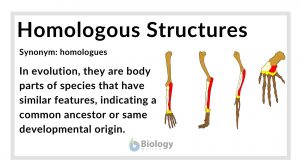
Homologous structures
Homologous Structures Definition What are homologous structures? In biology, homologous structures are physical features... Read More
Analogous structures
Analogous Structures Definition In evolutionary biology, analogous structures are biological structures having similar or... Read More
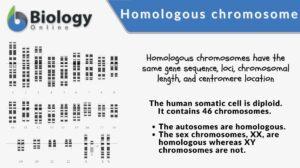
Homologous chromosome
A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and... Read More
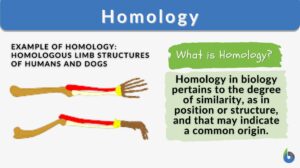
Homologous
Homologous Definition What is homologous? In general science, the word “homologous” is used to show a degree of... Read More
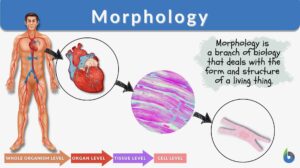
Morphology
Morphology Definition Morphology means the study of the shape and structure of living things from a biological perspective.... Read More
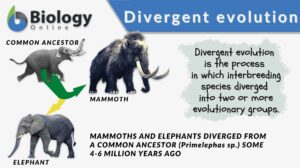
Divergent evolution
Divergent Evolution Definition Divergent evolution refers to the process by which interbreeding species diverged into two... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Convergent evolution
Convergent evolution definition What is convergent evolution? Convergent evolution is a concept in evolutionary biology... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Homogenous
What is homogenous? What does homogenous mean? The word homogenous has been derived from two Greek words that are... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
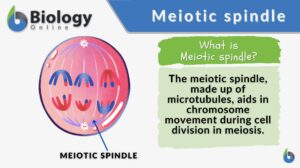
Meiotic spindle
Meiotic Spindle Definition The meiotic spindle refers to the spindle apparatus that forms during meiosis in contrast to... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Embryology
Embryology Definition Embryology is a branch of biology that deals with the topics concerning gamete formation... Read More
Synaptonemal complex
Definition noun, plural: synaptonemal complexes A complex protein structure that spans the region between the paired... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
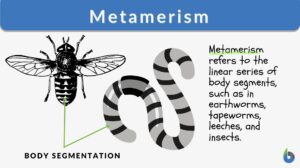
Metamerism
Metamerism Definition Metamerism is the repetition of homologous body segments. This type of development can be seen in the... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More